-
Title: Nabla-symbol
-
Series: Advent of Mathematical Symbols
-
YouTube-Title: Advent of Mathematical Symbols - Part 3 - Nabla-symbol
-
Bright video: https://youtu.be/mfHg_fHllEg
-
Dark video: https://youtu.be/Zg6GfgI-OwQ
-
Quiz: Test your knowledge
-
Dark-PDF: Download PDF version of the dark video
-
Print-PDF: Download printable PDF version
-
Thumbnail (bright): Download PNG
-
Thumbnail (dark): Download PNG
-
Subtitle on GitHub: aoms03_sub_eng.srt
-
Timestamps (n/a)
-
Subtitle in English
1 00:00:00,543 –> 00:00:03,871 The mathematical symbol for today is the Nabla symbol.
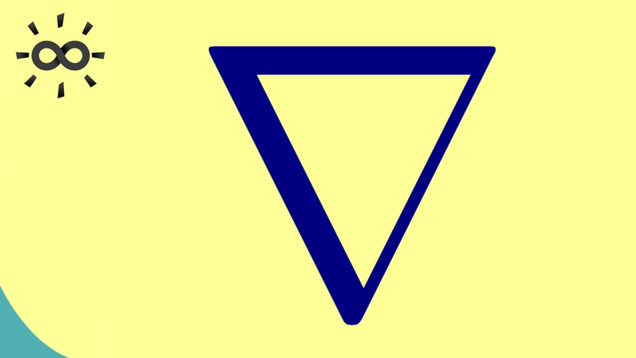
2 00:00:03,970 –> 00:00:06,395 Which is written as this triangle.
3 00:00:07,257 –> 00:00:11,929 It often occurs when you do vector analysis or multivariable calculus.
4 00:00:12,729 –> 00:00:17,336 Because there it can be used as an operator, which acts on functions.
5 00:00:18,257 –> 00:00:24,733 The definition is not so complicated. It’s just a vector, where the components are given by derivatives.
6 00:00:25,386 –> 00:00:29,421 So first we have the partial derivative with respect to the first variable
7 00:00:29,422 –> 00:00:31,000 Maybe it’s called “x_1”.
8 00:00:31,686 –> 00:00:36,695 Then the second component would be the partial derivative with respect to the second variable.
9 00:00:37,257 –> 00:00:41,728 Of course if you work in 3 dimensions, it ends with the third variable here.
10 00:00:42,271 –> 00:00:51,536 However in general, of course with n dimensions we just have n components and we end with the partial derivative with respect to the last variable.
11 00:00:52,257 –> 00:01:00,377 So what you should see here is, this is simply a short way to put all the partial derivatives, with first order into one object.
12 00:01:01,400 –> 00:01:07,857 Then formally you can calculate with this object we call Nabla, like it would be a normal vector.
13 00:01:08,557 –> 00:01:13,464 For example if we have the function that has two variable “x_1” and “x_2”.
14 00:01:14,043 –> 00:01:18,280 and now assume the function is just defined by “x_1” cubed.
15 00:01:18,480 –> 00:01:21,879 Then we can calculate the so called gradient of “f”.
16 00:01:22,857 –> 00:01:27,412 There we would write it as nabla f(x_1, x_2).
17 00:01:27,900 –> 00:01:31,043 Which in this case is a vector with two components.
18 00:01:32,043 –> 00:01:35,806 In the first one we find the partial derivative with respect to x_1
19 00:01:36,006 –> 00:01:38,769 Which means we have 3*x_1 squared.
20 00:01:39,714 –> 00:01:43,586 and in the second component we have the partial derivative with respect to x_2
21 00:01:43,672 –> 00:01:45,057 Which is 0.
22 00:01:45,743 –> 00:01:48,196 Ok, so this is the Nabla symbol.
23 00:01:48,396 –> 00:01:51,112 also often called the nabla operator.
24 00:01:51,312 –> 00:01:52,607 Thanks for listening.
-
Quiz Content
Q1: What would be the nabla symbol $\nabla$ in only one dimension?
A1: $\nabla = \frac{d}{dx}$
A2: $\nabla = 1$
A3: $\nabla = 0$
A4: $\nabla = \begin{pmatrix} 1 \ 0 \end{pmatrix} $
Q2: Consider the function $ f(x,y,z) = x^2 + y + z^3 $. What is $ \nabla f (x,y,z) $ in this case?
A1: $\begin{pmatrix} 2x \ 1 \ 3 z^2 \end{pmatrix}$
A2: $ 2x + 1 + 3 z^2 $
A3: $\begin{pmatrix} 2 \ 1 \ 3 \end{pmatrix}$
A4: $\begin{pmatrix} 1 \2x \ z^2 \end{pmatrix}$