-
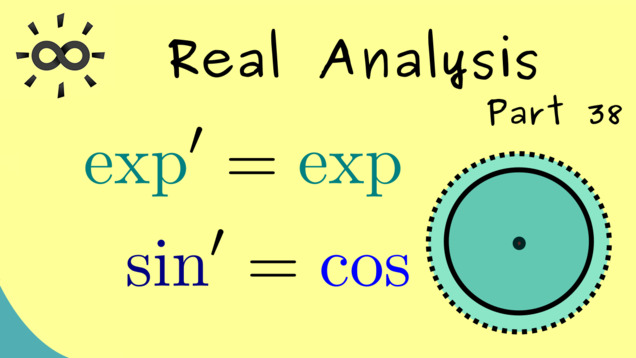
Title: Examples of Derivatives and Power Series
-
Series: Real Analysis
-
Chapter: Differentiable Functions
-
YouTube-Title: Real Analysis 38 | Examples of Derivatives and Power Series
-
Bright video: https://youtu.be/93i7uKScVvc
-
Dark video: https://youtu.be/LT7GIbfTCwo
-
Quiz: Test your knowledge
-
Dark-PDF: Download PDF version of the dark video
-
Print-PDF: Download printable PDF version
-
Thumbnail (bright): Download PNG
-
Thumbnail (dark): Download PNG
-
Subtitle on GitHub: ra38_sub_eng.srt missing
-
Timestamps (n/a)
-
Subtitle in English (n/a)
-
Quiz Content
Q1: What is the correct derivative for $f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ given by $f(x) = n , x^n$ for $n \in \mathbb{R}$?
A1: $f^\prime(x) = n x^n$
A2: $f^\prime(x) = n^2 x^n$
A3: $f^\prime(x) = n^2 x^{n-1}$
A4: $f^\prime(x) = n(n-1) x^{n-1}$
Q2: What is the correct derivative for the polynomial $f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ given by $f(x) = x^5 + 3 x^2 + 2 x$?
A1: $f^\prime(x) = 5 x + 3 x^2 + 2$
A2: $f^\prime(x) = 5 x^4 + 6 x + 2$
A3: $f^\prime(x) = 5 x^4 + 6 x^2 + 2$
A4: $f^\prime(x) = 5 x^3 + 6 x + 2$
Q3: Let the power series $f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ be given by $f(x) = \sum_{k=0}^\infty a_k x^k$. The radius of convergence is $\infty$. Which statement is not correct?
A1: For all $x \in \mathbb{R}$, the series $\sum_{k=0}^\infty a_k x^k$ is convergent.
A2: For all $x \in \mathbb{R}$, the series $\sum_{k=0}^\infty a_k x^k$ is absolutely convergent.
A3: The sequence of functions given by $g_n: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$, $g_n(x) = \sum_{k=0}^n a_k x^k$ is uniformly convergent to $f$.
A4: For all $c \in \mathbb{R}$, the sequence of functions given by $g_n: [-c,c] \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$, $g_n(x) = \sum_{k=0}^n a_k x^k$ is uniformly convergent to $f$ on the interval $[-c,c]$.
Q4: Let the power series $f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ be given by $f(x) = \sum_{k=0}^\infty a_k x^k$. The radius of convergence is $\infty$. Is $f$ differentiable?
A1: No, nowhere.
A2: Yes, but only for the point $x = 0$.
A3: Yes, everywhere.